How to set up a business in India from scratch?
Setting up a Business in India involves the following steps
-
Choosing the type of business
-
Business Registration Process
-
Central and State level Approvals / Compliances
-
Winding up of Business
Choosing the type of business
Foreign Investor can commence business in India in 3 forms:
-
Indian Company
-
Foreign Company
-
Limited Liability Partnership
Each of these types of companies is provided below.
-
Indian Company: Foreign company can set up a Joint Venture or Wholly Owned Subsidiary. JV/ Wholly Owned Subsidiary can be a Private Limited or Public Limited Company as per Companies Act, 2013.
-
Foreign Company: Foreign company can set up a Liaison Office, Branch Office or Project Office.
-
Liaison Office: Foreign Companies can set up a Liaison Office to represent the parent company in India.
Eligibility Criteria: Profit-making track record during the immediately preceding three financial years in the home country and net worth of not less than $ 50,000 or its equivalent.
Permitted Activities: LO can not undertake any commercial activity and acts as a channel of communication between the principal place of business or head office and entities in India. Its role is limited to collecting information about possible market opportunities and providing information about the company and its products to prospective Indian customers. It can promote export/import from/to India and also facilitate technical/financial collaboration between the parent company and companies in India. It cannot earn any income in India.
Remittances: NA
Validity: Generally for 3 years, except in the case of NBFCs and those entities engaged in the construction and development sectors, for whom the validity period is two years only
-
Branch Office: Foreign Companies can set up a Branch Office to undertake activities such as Export, Import, research, consultancy, etc.
Eligibility Criteria: Profit-making track record during the immediately preceding five financial years in the home country and net worth of not less than $ 100,000 or its equivalent.
Permitted Activities: BO can be set up by foreign companies. The permitted activities include export/import of goods; rendering professional or consultancy services; carrying out research work, in which the parent company is engaged; promoting technical or financial collaborations between Indian companies and parent or overseas group company; representing the parent company in India and acting as buying/selling agents in India; rendering services in information technology and development of software in India; rendering technical support to the products supplied by the parent/ group companies and foreign airline/shipping company.
There is a general permission to non-resident companies for establishing BO in the Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to undertake manufacturing and service activities subject to:
-
-
BOs comply with Chapter XXII of the Companies Act, 2013
-
BOs are functioning in those sectors where 100% FDI is permitted
-
BOs function on a stand-alone basis
-
Remittances: Permitted to remit profits net of applicable taxes and on submission of requisite documents.
Validity: Nil
-
Project Office: Foreign Companies can set up a Project Office to conduct activities as per contract to execute project.
Eligibility Criteria: Nil
Permitted Activities: PO can be set up to execute specific projects in India and cannot undertake or carry on any activity other than the activity relating and incidental to the execution of the project.
Remittances: Intermittent remittances by companies pending winding-up permitted s.t. satisfaction of AD Category 1 bank.
Validity: As per the tenure of the project
-
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): Foreign companies can set up a business in India as LLP subject to provisions of LLP Act, 2008.
An analysis of types of permitted business establishment in India are provided below.
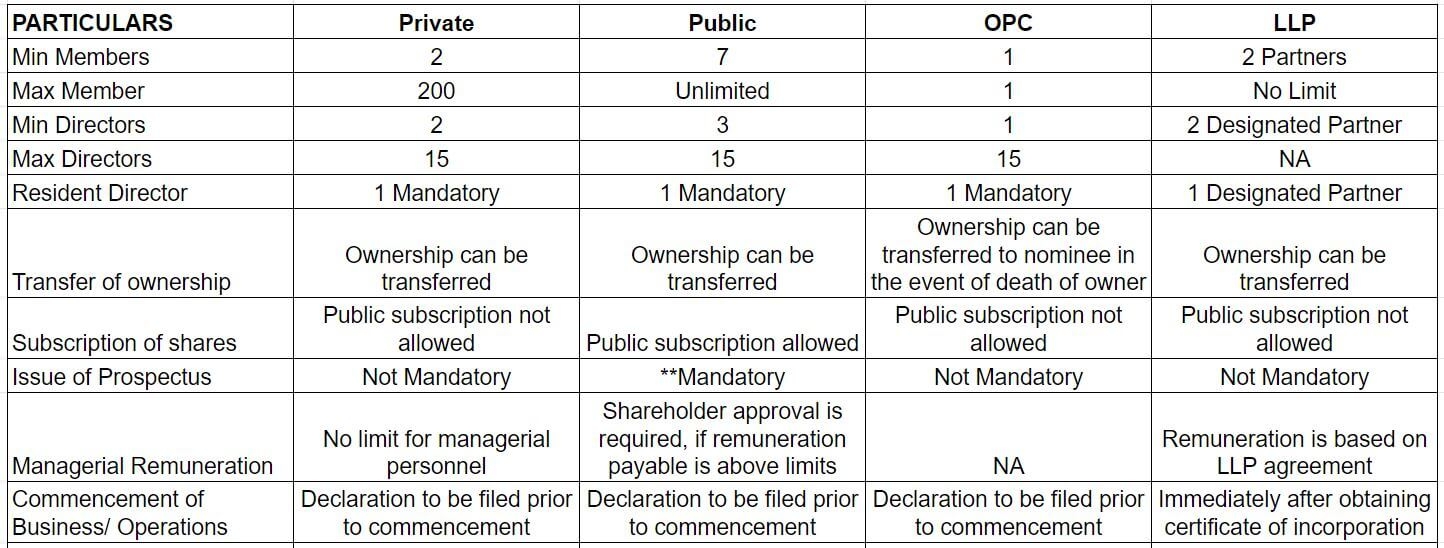
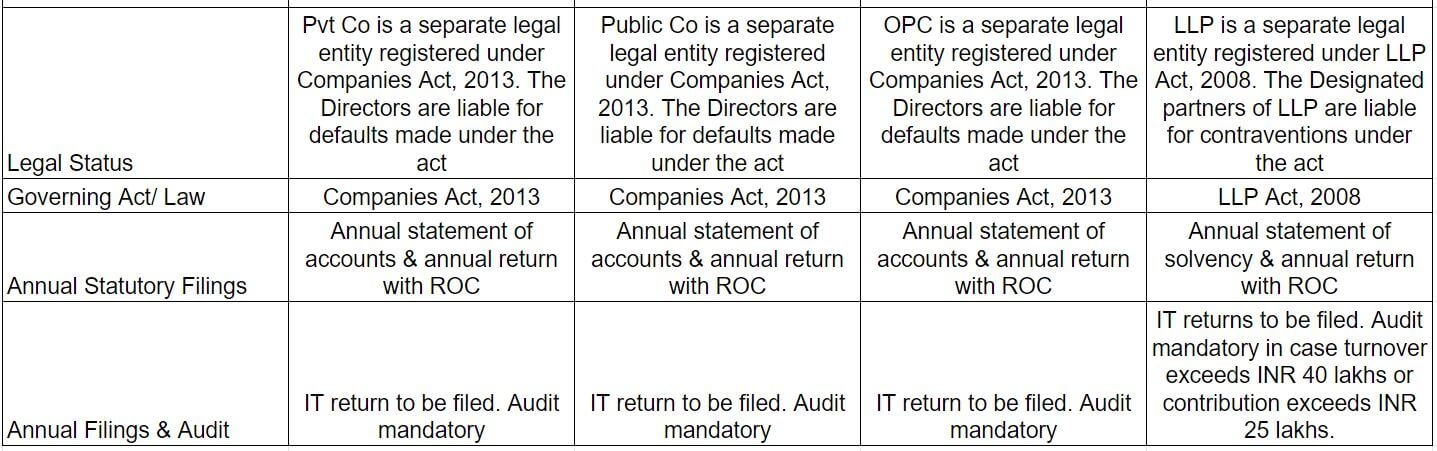
Business Registration Process
Businesses can be registered as a Company or LLP.
Business Registration Process as a Company
Follow the below steps to register the business as a Company.
-
Check availability of name / registered trademark for incorporation of the company. Further to this, reserve name of the proposed company through online service RUN on MCA website. The name can also be applied through SPICe.
-
Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for at least one proposed designated Directors of the Company. DIN for proposed Directors can only be applied for through form SPICe.
-
Form INC 32 (SPICe) are to be duly filled and submitted to RoC for incorporation of the company. PAN and TAN are shall be auto-generated based on details filed in the SPICe form
-
Filing of electronic Memorandum of Association (eMoA - INC 33) in SPICe . For foreign subscribers physical MoA to be executed and attached
-
Filing of electronic Articles of Association (eAoA- INC 34) in SPICe . For foreign subscribers physical AoA to be executed and attached
-
SPICe upload and fee payment is confirmed by MCA
-
Central Registration Centre (CRC) verifies/ scrutinizes all the documents and forms and may suggest few changes to be made in the attachments or form itself. One needs to make necessary changes accordingly
-
Obtain the certificate of incorporation (CoI). CIN, PAN & TAN numbers are allotted at the time of registration
-
A company having share capital is required to file a declaration of receipt of subscription amount and verification of registered office within 182 days of incorporation and prior to commencement of business.
Business Registration Process as an LLP
Follow the below steps to register the business as an LLP.
-
Obtain class 2 or class 3 Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for designated partners of LLP
-
For a quick search on already existing names of LLP a facility is provided by MCA to check list of similar/closely resembling names of existing companies/LLPs. Trademark is also to be checked
-
Filing the proposed name of LLP for approval from the Registrar of Companies through RUN – LLP and can also be done through FiLLiP
-
FiLLiP is to be duly filled and submitted to RoC for incorporation of LLP. For Foreign LLP (FLLP) Form 27 is to be filed in and digitally signed by FLLP (DPIN must be obtained through FiLLiP.
-
Form 3 (Information with regard to LLP agreement and changes, if any made therein) to be filled within 30days of incorporation of LLP
Central Level Compliances
The following steps are involved in setting up legal existence of the Company.
-
Approval for proposed Company Name
For LLP name search facility (of existing companies/ LLPs) is available on the MCA portal. The system will provide the list of similar/closely resembling names of existing companies/ LLPs based on the search criteria filled up. For registration of the name, RUN - LLP to be filed.
The applicant must file e form RUN with the Central Registration Center (CRC), India for approval of name.
The name reserved for the company shall be available for adoption of the name for a period of 20 days. In the case of laps of the said period, fresh approval needs to be taken from RUN or RUN - LLP is to be taken. For LLP name is reserved for 3 months. In case of a change of name of the company, the reserved name is available for 60 days.
-
Consent to establish & operate
Issue of Certificate of Incorporation by CRC - Once all the Forms are duly approved by CRC, the digitally signed “Certificate of Incorporation” is issued. In the Case of LLP, LLP agreement is required to be signed and submitted to ROC within 30 days of incorporation of LLP.
Once the Incorporation Certificate is received, LLP can start its operations.
-
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for proposed Directors
DSC can be obtained by approaching Certifying Authorities (CAs) with original supporting documents and self-attested copies. A licensed Certifying Authority (CA) issues the digital signature. Certifying Authority (CA) means a person who has been granted a license to issue a digital signature certificate under Section 24 of the Indian IT-Act 2000.
-
Filing of e-forms with CRC
SPICe is duly filled and submitted to CRC for incorporation of the company. MCA form FiLLiP for LLP would be required. Form 27 is required for Foreign LLP (FLLP).
-
Finalization of supporting documents
Filing of electronic Memorandum of Association (eMoA- INC 33) & Articles of Association (eAoA- INC 34). Payment of stamp duty/ filing fees. In case of foreign subscribers, physical MOA and AOA are to be filled in.
-
Grant for BIS License
The applicant has to submit the application in the prescribed Form & Self Evaluation-cum-Verification Report along with prescribed documents and original test report(s) taxes) for considering grant of the license under Product Certification Scheme of BIS.
-
Obtain Director Identification Number (DIN)
DIN is a unique identification number issued by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), for a designated partner of an existing LLP or a person intending to become a director of a company.
DIN can be obtained by filing application Form DIR-3 online.
All designated partners of the proposed LLP shall obtain “Designated Partner Identification Number (DPIN) / Director Identification Number (DIN)” through FiLLiP & proposed company through SPICe (if DIN is not available)
Note – Application for DIN (for a person proposed to be appointed as a Director of an existing company or LLP) to be filed in Form DIR-3. Change in particulars to be intimated in Form DIR-6 within 30 days
-
Obtain Permanent Account Number (PAN)
PAN number shall be allotted based on the information filled in Form SPICe at the time of incorporation of a company.
-
Quality Marking Certificate
Quality Marking certificate is provided by Quality Marking Centre of the State Government.
-
Registration for Tax Account Number (TAN)
TAN number shall be allotted based on the information filled in Form SPICe at the time of incorporation of a company.
-
Verification of documents
After payment of all fees & stamp duties, CRC scrutinizes all forms and may suggest changes in forms and/or attachmments.
State Level Compliances
Starting/Registering a unit in State
-
Approval for State Incentives (Optional): Apply for state government incentives/ customized package scheme for Mega projects as per state policies (Optional)
-
IEM/ EM Registration: All industrial undertakings exempt from the requirements of industrial licensing, including existing units undertaking substantial expansion, are required to file information in the prescribed form for Industrial Entrepreneurs Memorandum (IEM), i.e. “Form IEM”, with the Secretariat of Industrial Assistance (SIA), Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Government of India, and obtain an acknowledgement. No further approval is required.
Optional for all Micro and small enterprises; Service sector medium enterprises; mandatory for manufacturing sector medium enterprises.
-
MSME Registration: MSME Registration is an optional registration under the MSMED Act that provides Micro, Small and Medium sized enterprises with a host of benefits and access to subsidies and schemes.
-
Registering / categorization of unit in State: For starting a manufacturing unit in any state, the first step for the company is to register themselves as MSME or Mega or Large Projects. The criteria to categorize a unit into MSME or Mega Project or Ultra Mega Project is defined the in respective industrial policies of states. This would benefit the units to apply for various incentives available under state government Policies/ Scheme in addition to other specific policies.
Pre Commissioning Phase
-
Acquisition of Land: Application to respective State DI/ State Industrial Development Corporation (SIDC)/ Infrastructure Corporation/ Small Scale Industrial Development Corporation (SSIDC)
-
Approval for lifts & Escalator: Lift and escalator approval needs to be obtained from local state authority. Approval is given for installation and operation is accorded separately.
-
Building Plan Approval: An approval from development authority/ local nodal authority for sanction of building plans/ building permit under the provisions of Building Byelaws, Master plan and Local Body Acts. The Building approval comprises of the building plan and the layout approval for the construction of the building. The applicant has to get approval of layout plan from concerned authorities before starting construction of. Intimation of Disapproval or IOD basically states conditions that needs to be complied with during different phases of Under Construction Project. Post this the applicant received commence certificate to commence construction.
-
Consent to Establish: Consent to establish is required from Environment and pollution control board for starting the building construction activity of the unit. An application is to be made to concerned bodies at the state pollution board and central level for environment clearance.
-
Environment, Forest and Wildlife Clearance: Application for environment clearance (EC) needs to be made at the online platform by MoEF. Proposals requiring EC clearance under EIA notification 2006. Proposals requiring only CRZ Clearance under CRZ Notification 2014. Proposals requiring both clearances i.e. EC clearance (Category A and Category B both) under EIA notification 2006 and CRZ Clearance under CRZ notification 2011.Environment Clearance is a two-stage process. Stage 1 - Grant of ToR (If, after accepting category A or category B proposals, Ministry/ SEIAA do not take any decision within one month, then, Standard TOR is accorded automatically to the proposal. Stage 2- Grant EC - TOR accorded proposals, Proposals without TOR.
-
Factory Layout Plan Approval: Under the Factory Act, 1948 approval for Factory Layout Plan is required. It is usually granted by the Labour’s Department of each state however the competent authority may vary from state to state. The approval is granted within 60 days for chemical factory and 45 days for other factories subject to the specific criteria met by the competent authority of the state. The layout plan approved is non – transferrable.
-
Factory registration: Licensing is done under Industries (Development & Regulation) Act 1951. only five industries are under compulsory licensing:
-
Electronic aerospace and defence equipment
-
Industrial explosives including detonating fuses, safety fuses, gun powder, nitrocellulose and matches
-
Cigars and cigarettes of tobacco and manufactured tobacco substitutes
-
Specified hazardous chemicals i.e. (i) hydrocyanic acid and its derivatives (ii) Phosgene and its derivatives and (iii) Isocyanates & disocyanates of hydrocarbon not elsewhere specified (example methyl Isocyanates)
-
Distillation and brewing of alcoholic drinks.
-
Industrial undertakings can apply through online application Form IL. Else IEM has to be availed The step by step guide for availing IEM illustrated at the link
-
Industrial License: Industrial licenses are regulated by the IDRA, 1951 Act, and are approved by the Secretarial of Industrial Assistance (SIA) on the recommendation of the licensing committee. Businesses planning to establish industries to produce any of the following items in India must obtain a compulsory license:
-
Distillation and brewing of alcoholic drinks;
-
Cigars and cigarettes of tobacco and manufactured tobacco substitutes;
-
Electronics and aerospace and defence equipment;
-
Industrial explosives including detonating fuses, safety fuses, gun powder, nitrocellulose and matches; and
-
Hazardous chemicals including items hazardous to human safety and health and thus fall for mandatory licensing.
-
Industrial undertakings can apply through online application Form IL .
-
Permission for Land Use: Applicable in case industry located outside an industrial area. Concerned departments to be contacted are the following.
-
State Directorate of Industries (DI)
-
Department of Town and Country Planning
-
Local authority/ District Collector
-
Pollution Board: Application to State Pollution Boards before commencement of construction activities and production activities under Water Act and Air Act for Consent to Establish and CTO respectively is to be made There are 4 categories of industries-
-
Red – Industries having pollution index score of 60 and above
-
Orange- Industries having pollution index score of 41 to 59
-
Green - Industries having pollution index score of 21 to 40
-
White- Industries having pollution index score up to 20
-
Note- The approval is granted by state and compliance procedure may vary from state to state
-
Power for construction: Application to State Electricity Distribution Company for sanction of power supply for low tension (LT), high tension (HT), or Extra High Tension connection as applicable during the construction phase.
-
Provisional Fire Approval: Provisional Fire Safety Approval from State Fire and Safety department.
-
Registration of Boilers: As per the Boiler Act 1923, registration of Boiler is mandatory compliance. Permission for registration is granted post successful inspection. Provisional registration is granted by the competent authority for the period of 6 months, within which the final inspection (upon request) is undertaken.
For further details, please refer to this link.
-
Registration under BOCW Act: Under the Building and other Construction Workers Act, 1996 approval required during pre and post commissioning stage. It is usually granted by the Labour’s Department of each state however the competent authority may vary from state to state .
The approval is granted within 30 days subject to the specific criteria met by the competent authority of the state.
-
Registration under Contract Labour Act 1970: Under the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970 approval required. It is usually granted by the Labour’s Department of each state however the competent authority may vary from state to state.
The approval is granted within 30 days subject to the specific criteria met by the competent authority of the state.
Post Commisioning Phase
-
Authorization for hazardous waste: Application to State Pollution Control Boards for Collection/ Reception/ Treatment/ Transport/ Storage and Disposal of Hazardous waste.
-
Building Completion certificate: A completion certification (CC) is a critical and mandatory legal document that a builder should obtain from Application to Town and Country Planning , or Local municipality , development authority or agricultural department or other local bodies such as Nagar Nigam or Gram Panchayat as applicable) with plan, scrutiny fees and land allotment copy.
After the completion of a project, the local authority inspects and evaluates the premise against the approved building plan and awards the completion certificate, if all the rules are satisfied.
-
Central Excise Registration: The application for registration is to be filed with the Superintendent of Central Excise having jurisdiction over the premises in respect whereof the registration is to be obtained.
Note – Applicability of Excise is for liquor and petroleum based units.
-
Consent to Operate: Consent to operate is obtained from Pollution control board of the respective states. It is required in both pre-commissioning stage. It is subject to renewal from time to time.
-
Customs- Special Valuation Branch: Special Valuation Branch (“SVB”) is a branch of the Custom House that specializes in investigating the transactions involving relationship between the supplier and the importer. The detailed working and functions of the branch can be accessed at link.
-
Employee Registration with ESIC: Employees' State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) provides monetary and medical benefits to Employees in case of sickness, maternity and employment injury and to make provisions for related matters. Form 01 should be used by employers to register with ESIC.
-
Employer Registration with EPFO: The Employees' Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) provides social security benefits to Employees of establishments on which the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act 1952. Online registration for EPFO can be done through link.
-
Final Fire Approval: Final Fire approval needs to be taken by local state authority.
-
GST Registration: Any business whose turnover exceeds the threshold limit of INR 20 lakhs (INR 10 lakhs for North Eastern and hill states) will have to register under GST. Businesses registered under any of the pre-GST laws: VAT, Excise/Service Tax have to register under GST by default.
Any business can get registered under GST by applying via the GST Online Portal or at GST Seva Kendra set up by the Government of India. Fill Form-part A (PAN, Mobile and email id. The portal verifies your detail via OTP. Upload the document as per business type. Fill Form-part B using the received number through OTP. Application reference number shall be received via mobile/ email. The GST officer verifies your application/ document. In case more information/ documents are asked through Form GST-REG-03 details have to be shared through Form GST-REG-04 within 7 working days. GST officer approves application and GSTIN within 7 working days.
-
Importer Exporter Code (IEC): Import Export (IE) Code is a registration required for persons importing or exporting goods and services from India. IE Code is issued by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), Ministry of Commerce and Industries, Government of India. IE Codes when issued can be used by the entity throughout its existence and doesn't require any renewal or filing.
IE Code application must be made to the Directorate General of Foreign Trade along with the necessary supporting documents.
-
Power: Application to State Electricity Distribution Company for sanction of power supply for low tension (LT), high tension (HT), or Extra High Tension connection as applicable.
-
Professional Tax Registration: According to section 5 of the Profession Tax Act, every employer (not being an officer of the government is liable to pay tax and shall obtain a certificate of registration from the prescribed authority. The company is required to apply in Form I to the registering authority.
-
Shops & Establishment Act: Registration under Shop & Establishment is provided by state government.
-
Trademark/ Brand Registration: Trademark registration provides legal right of exclusivity for the use of mark to the owner of the mark. Trademark registration involves multiple steps. A step by step guide for registration of trademark is detailed at link.
-
Water Connection: State Industrial Development Corporations for approval for water connections; to State Industrial Promotion Boards (where applicable) where source of water is river/ canal/ dam; and to Central Ground Water Commission in case of groundwater extraction.
Winding Up of Business
In case, winding up of Business is required, you can follow the below steps to wind up your business in India.
-
Prepare declaration of solvency and hold board meeting
-
Obtain shareholders, creditors approval & appoint liquidator
-
Public notice inviting claims
-
Intimate Statutory authorities and banker
-
Submit preliminary report on verification of claims by liquidator
-
Realise assets, discharge liabilities and repatriate funds if any
-
Filing application for winding up
-
NCLT to pass dissolution order
FAQs
You can find a list of common Business queries and their answer in the link below.
Business queries and its answers
Tesz is a free-to-use platform for citizens to ask government-related queries. Questions are sent to a community of experts, departments and citizens to answer. You can ask the queries here.
Ask Question
 Share
Share




